지정한 폴더에서 wav 파일만 읽어와 해당 wav 파일의 길이와 누적 길이를 출력하여,
다음과 같은 형태의 csv 파일로 저장하는 코드가 필요했다.
| num | name | duration | accumulation |
| 넘버 | 파일 이름 | 파일 길이 값 | 파일 길이 누적 값 |
작업했던 폴더 구조의 일부는 다음과 같다.
HOME
├── folder1
├── sub_folder1
├── img
└── .jpg
├── video
└── .mp4
└── wav
└── .wav
folder는 총 3개가 있고,
그 안에 400개가 넘는 sub_folder가 있고,
하나의 sub_folder 안에는 이미지, 영상, 오디오 각각의 폴더와 함께 데이터가 들어가 있다.
처음엔 구조를 훑어만 봐서
path = '/home/'
file_list = os.listdir(path)
file_list_path = [file for file in file_list if file.endswith(".wav")]
습관적으로 os.listdir() 을 썼고,
os.listdir()은 지정한 디렉토리 내에서만 움직이기 때문에 당연히 될 리가 없었다.
하위의 하위까지 내려가지 않기 때문에.
그래서 os.walk() 를 사용했다.
os.walk()
하위의 폴더들을 for문으로 탐색할 수 있다.
인자로 전달된 path에 대해 root, dirs, files 의 값을 튜플 형태로 넘겨준다.
root는 그 폴더의 path,
dirs와 files는 root의 하위 폴더와 파일들에 대한 리스트이다.
감이 잘 오지 않으면 print()를 찍어보면 된다. 디버깅도!
코드의 흐름은 다음과 같다.
import os
import wave
import glob
path = '/home/'
acc = 0
num = 0
g = open('/home/wav_info.csv', 'w')
1. 누적 값과 넘버는 증감이 되야 하기 때문에 acc=0 과 num=0 으로 셋팅했다.
2. home 디렉토리에 wav_info라는 제목의 csv 포맷 파일을 쓰기 모드로 열어준다.
| 옵션 | 의미 | 설명 |
| r | read | 읽기 모드 |
| w | write | 쓰기 모드, 파일에 이미 내용이 있다면 기존 내용은 사라지고 덮어 쓰여짐 |
| a | append | 추가 쓰기 모드, write는 덮어쓰지만 'a' 기존 내용 이어서 추가 됨 |
| x | create | 파일이 없으면 파일 생성 후 쓰기 모드, 파일이 존재하면 에러남 |
for root, dirs, files in os.walk(path):
for name in files:
if name.endswith(".wav"):
with wave.open(root + "/"+ name, 'r') as f:
num += 1
frames = f.getnframes()
rate = f.getframerate()
duration = frames / float(rate) # duration(sec) = frame / rate
print(duration)
acc += duration
g.write("%s,%s,%0.1f,%0.1f"%(str(num), name, duration, acc))
g.write('\n')
g.close()
3. 위에서 설명했듯이 하위의 폴더들을 for문으로 탐색하는 os.walk를 이용했다.
인자로 전달된 path에 대해 files 값 중 name이 '.wav' 로 끝나는 파일만 가져오고,
wav 포맷 데이터의 frame과 rate를 각각 구해준 후,
frame을 rate로 나눠주면 초 단위의 길이를 구할 수 있다.
acc += duration 은 acc = acc + duration 이기 때문에 길이 누적 값을 구할 수 있다.
4. duration과 acc는 float의 형태로 소수점 첫번째 짜리까지만 필요하기 때문에 %0.1f 로 설정.
만약 소수점 두번째 자리까지 필요하다면 %0.2f 로 작성하면 된다.
5. 위에서 파일을 write를 해줬으면 반드시 close()도 해주기.
위의 흐름을 합친 최종 코드는 다음과 같다.
import os
import wave
import glob
path = '/home/'
acc = 0
num = 0
g = open('/home/wav_info.csv', 'w')
for root, dirs, files in os.walk(path):
for name in files:
if name.endswith(".wav"):
with wave.open(root + "/"+ name, 'r') as f:
num += 1
frames = f.getnframes()
rate = f.getframerate()
duration = frames / float(rate) # duration(sec) = frame / rate
print(duration)
acc += duration
g.write("%s,%s,%0.1f,%0.1f"%(str(num), name, duration, acc))
g.write('\n')
g.close()
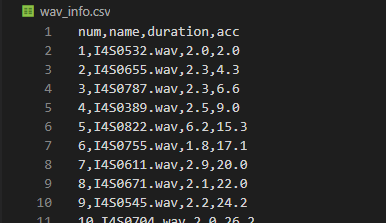
csv파일로 잘 나왔다.
끝!
더 자세한 내용은
WAV files docs
https://docs.python.org/3.8/library/wave.html#wave-read-objects
wave — Read and write WAV files — Python 3.8.13 documentation
wave — Read and write WAV files Source code: Lib/wave.py The wave module provides a convenient interface to the WAV sound format. It does not support compression/decompression, but it does support mono/stereo. The wave module defines the following functi
docs.python.org
formatting docs
https://docs.python.org/3/tutorial/inputoutput.html
7. Input and Output — Python 3.10.3 documentation
7. Input and Output There are several ways to present the output of a program; data can be printed in a human-readable form, or written to a file for future use. This chapter will discuss some of the possibilities. 7.1. Fancier Output Formatting So far we
docs.python.org
'code > python' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [python] 자료형 정리 3 - 튜플 (0) | 2022.03.30 |
|---|---|
| [python] 자료형 정리 2 - 리스트 (0) | 2022.03.29 |
| [python] 자료형 정리 1 - 문자열 (0) | 2022.03.29 |
| [MoviePy] python에서 동영상을 GIF로 변환하기 mp4 to gif (0) | 2022.03.20 |
| [logging] python logging 으로 log 파일 만들기 (0) | 2022.03.15 |


